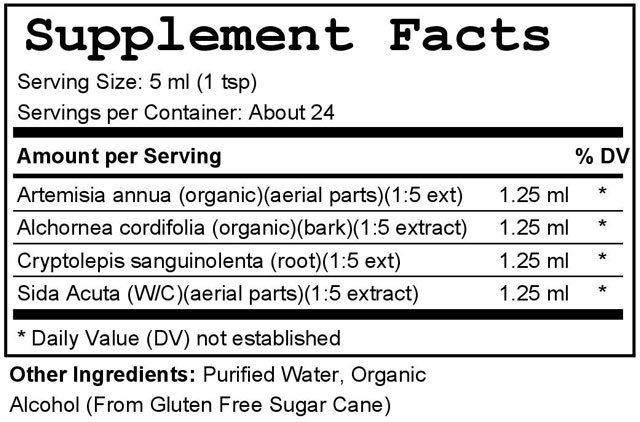
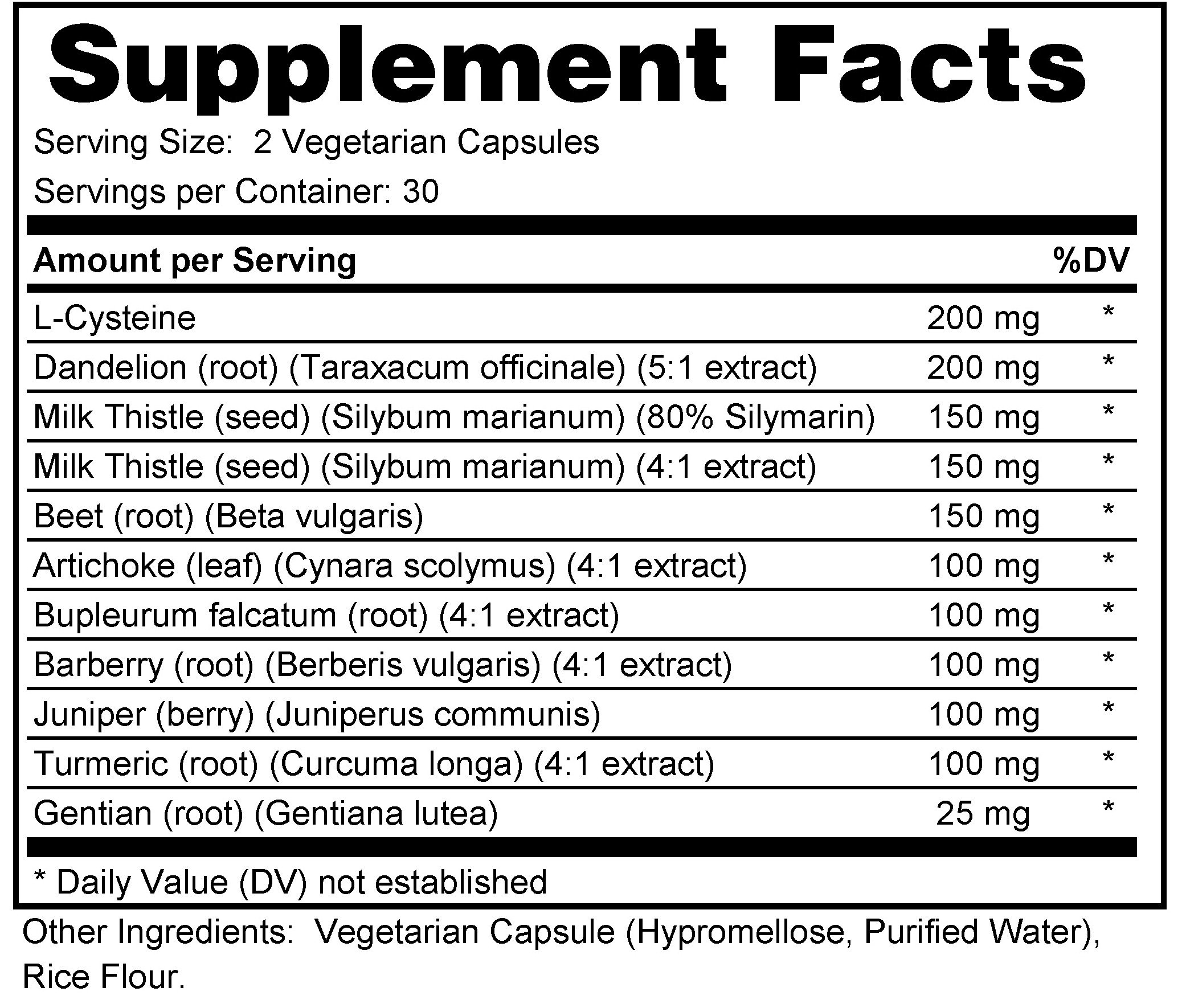
Cordyceps militaris, a species of entomopathogenic fungus, contains bioactive compounds, including cordycepin, cordycepic acid, polysaccharides, and adenosine, which have demonstrated diverse pharmacological properties. Studies have suggested that Cordyceps militaris extracts may possess antimicrobial properties against certain tick-borne pathogens, indicating potential relevance in combating tick-borne infections, including Borrelia burgdorferi, the causative agent of Lyme disease. Additionally, the fungus’s constituents have exhibited immunomodulatory effects, enhancing the activity of immune cells and promoting a balanced immune response. These immunomodulatory properties may be beneficial in supporting the body’s defense against tick-borne diseases.
Properties:
- Immunomodulatory Effects: Cordyceps sinensis has been found to possess immunomodulatory properties, meaning it can help regulate and balance the immune response. Tick-borne diseases can dysregulate the immune system, leading to either an excessive or suppressed immune response. Immunomodulation may play a role in restoring immune function and promoting recovery.
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Inflammation is a key contributor to symptoms and tissue damage in tick-borne diseases. Cordyceps has been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties, which may help alleviate inflammation associated with these diseases.
- Antioxidant Effects: Cordyceps contains bioactive compounds with antioxidant properties. Antioxidants help neutralize harmful free radicals and reduce oxidative stress. Tick-borne diseases can induce oxidative stress, leading to tissue damage and inflammation. Antioxidants may have a protective effect in this context.
- Overall Health Support: Cordyceps is often associated with promoting overall health and well-being. Its potential benefits on immune function, energy metabolism, and respiratory health may indirectly support individuals dealing with tick-borne diseases
Studies:
- “Immunomodulatory Activities of Polysaccharides from Cordyceps sinensis: A Review” (2018): This review article discusses the immunomodulatory activities of polysaccharides derived from Cordyceps sinensis. It highlights the potential of Cordyceps sinensis polysaccharides to enhance immune function, regulate inflammatory responses, and modulate the immune system. While not specifically focused on tick-borne diseases, these immunomodulatory effects may have implications for supporting immune function in the context of tick-borne diseases.
- “Antioxidant and Immunomodulatory Activities of Cordyceps sinensis Polysaccharides in Mice” (2012): This study investigated the antioxidant and immunomodulatory activities of Cordyceps sinensis polysaccharides in mice. The researchers found that the polysaccharides exhibited antioxidant effects and enhanced certain immune parameters, suggesting their potential in supporting immune health. While not directly related to tick-borne diseases, these findings suggest that Cordyceps sinensis may have immunomodulatory properties that could be beneficial in managing such diseases.
- “Effect of Cordyceps sinensis on the Proliferation and Apoptosis of Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells” (2014): This study examined the effects of Cordyceps sinensis on human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). The researchers found that Cordyceps sinensis extract promoted the proliferation of PBMCs and inhibited apoptosis (cell death). While not specific to tick-borne diseases, these findings suggest potential immune-stimulating effects of Cordyceps sinensis that could be relevant in managing such diseases.